For the best user experience of the next part, please use tablet or desktop

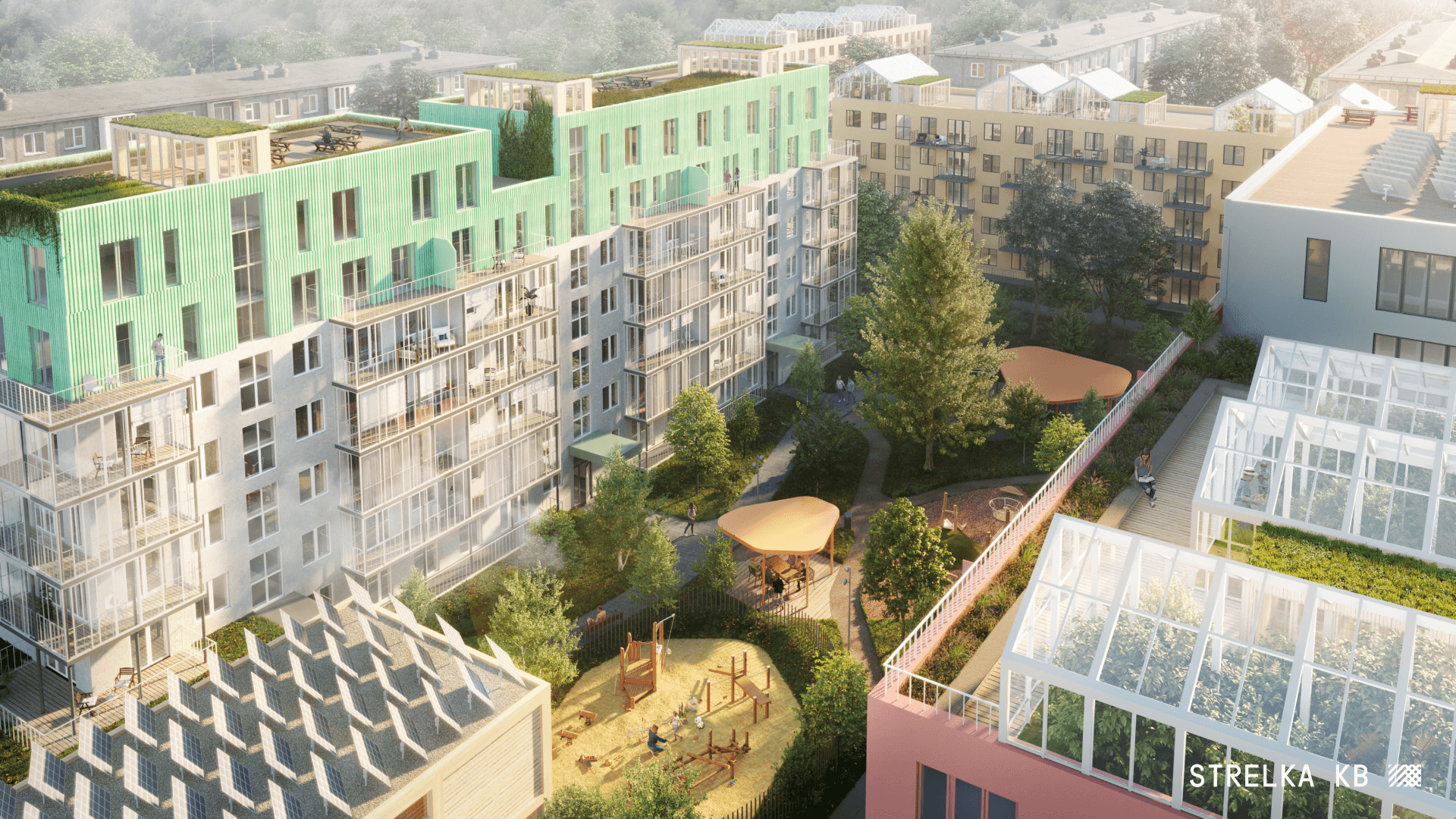
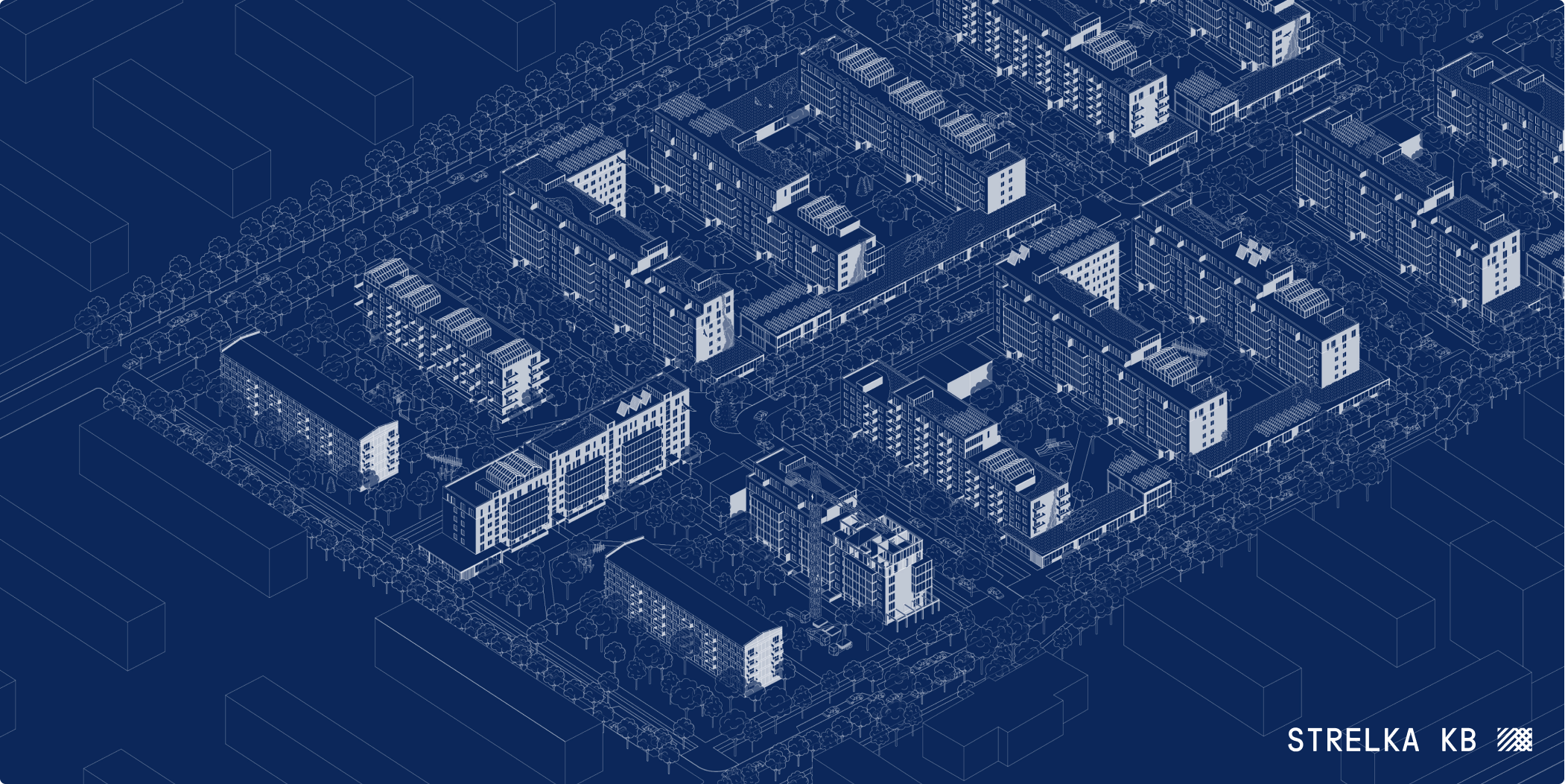
Existing plot
The renovation affects the microdistrict development formed in 1960-1980 and formed primarily by five-storey panel, block and brick sectional houses. Among the main disadvantages of such areas are the monotony of architectural solutions, low density, shortage of public service facilities, as well as poor quality of public spaces and landscaping of adjacent territories. At the same time, the key positive feature of such areas is the abundance of greenery, as well as the scale of development.
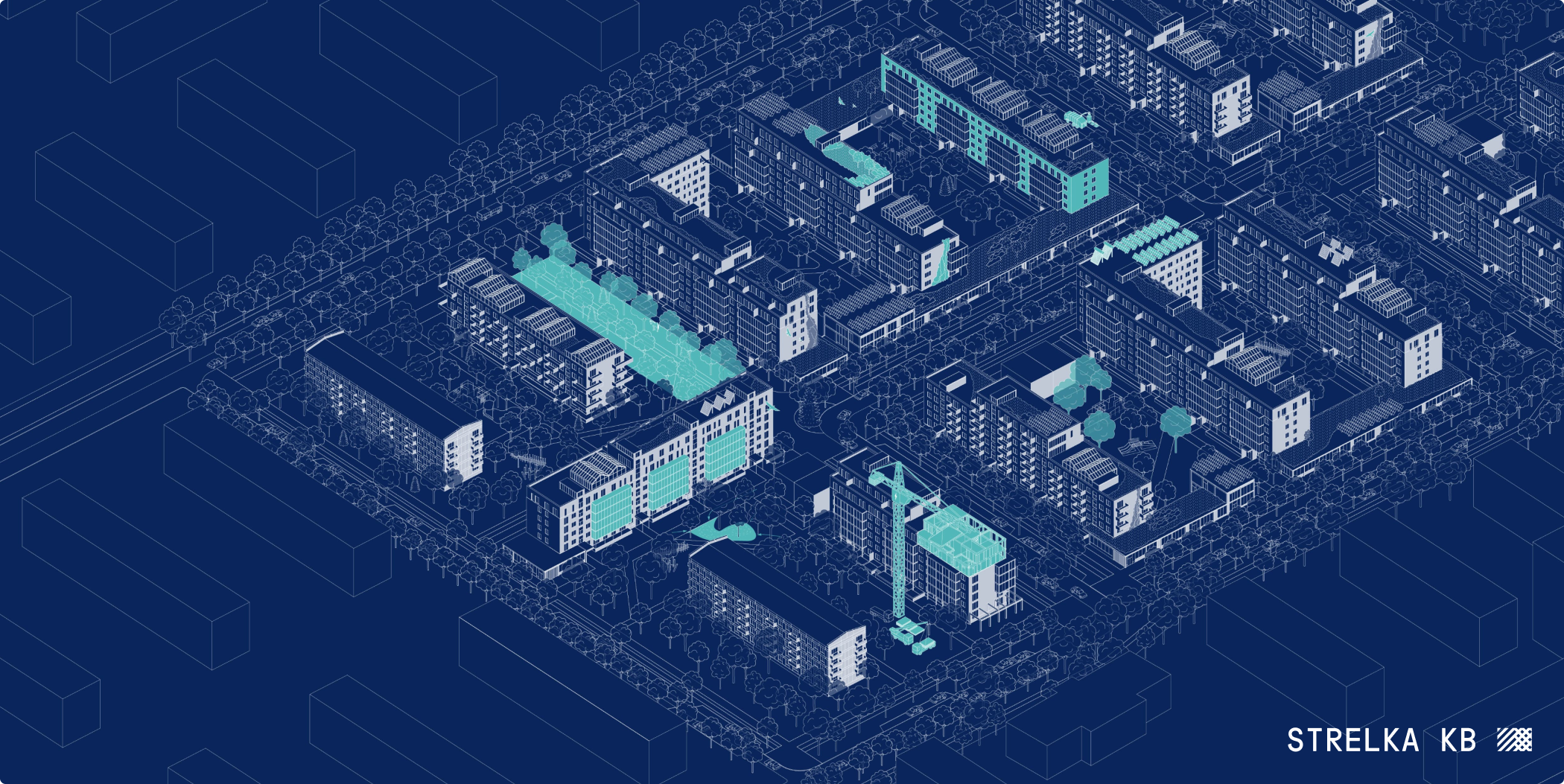

E4: Climate Resilience and vibrant ecosystems
E5: Zero waste
E2: Low energy consumption
E3: Sustainable utilization of available resources
E4: Climate Resilience and vibrant ecosystems
E2: Low energy consumption
E4: Climate Resilience and vibrant ecosystems
E4: Climate Resilience and vibrant ecosystems
E1: Carbon neutral materials and technologies
E1: Carbon neutral materials and technologies
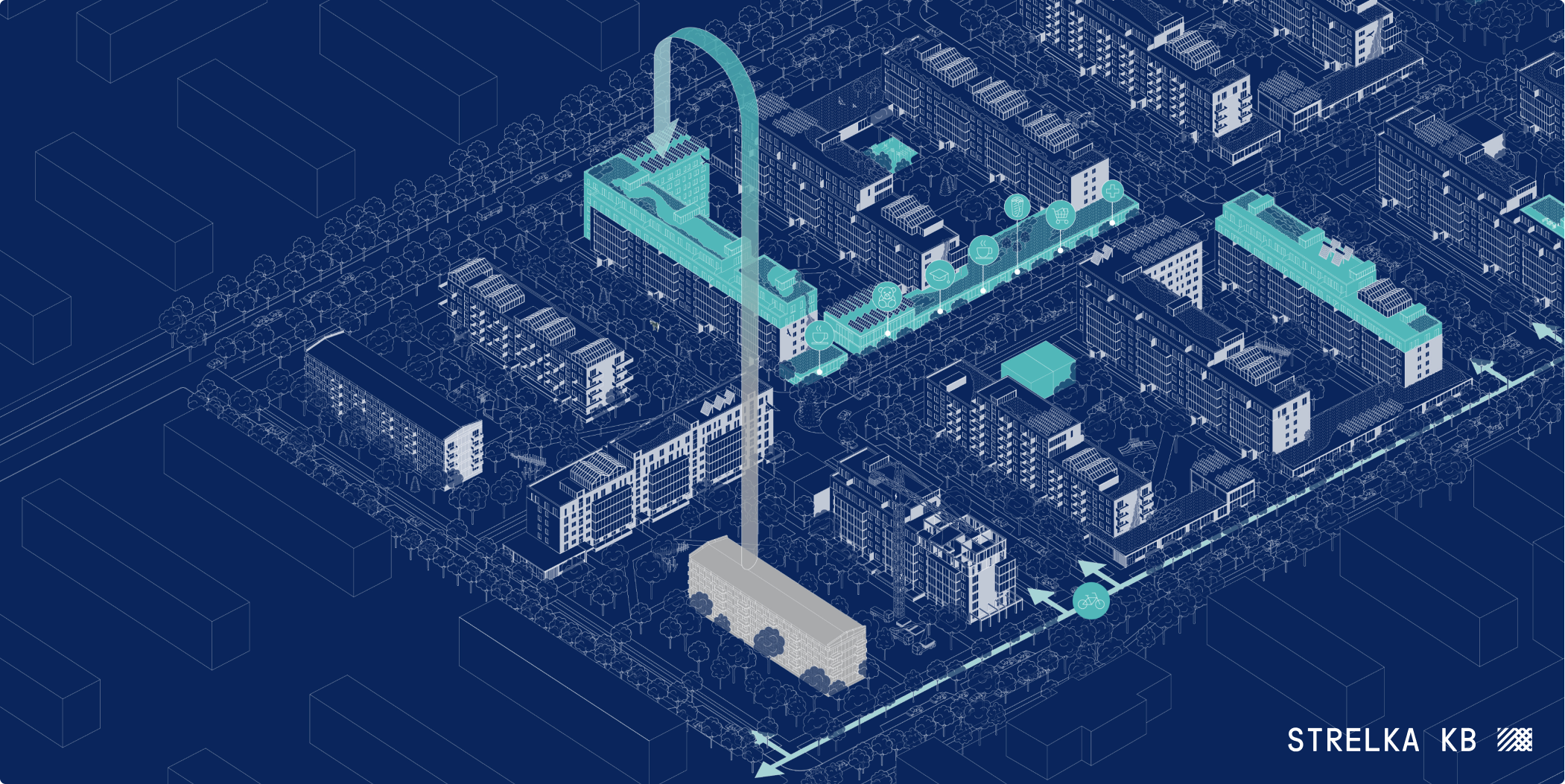
Environmental solutions
Set of environmental solutions are implemented in order to preserve and maintain the ecological balance of territories, reduce the negative impact on the environment, maintain biological diversity, as well as facilitate the effective use of available resources necessary for the needs of residents.
S5: Localism
S3: Healthy spaces and inclusivity
S2: Diverse social groups
S1: Mixed uses and programmes
S2: Diverse social groups
S3: Healthy spaces and inclusivity
S4: Public-Private balance
Social solutions
Group of solutions that focus on social improvements driven by a comfortable environment with a variety of opportunities for recreation and leisure within a minute's walk from home. Such solutions make it possible to turn sparse areas into local centres of urban life, forming conditions for the development of social ties among residents.
G3: Stimulation renovation
G4: Mixed financing
G4: Mixed financing
G2: Public driven design
G1: Acceleration of the renovation
G1: Acceleration of the renovation
G5: Local economy facilitation
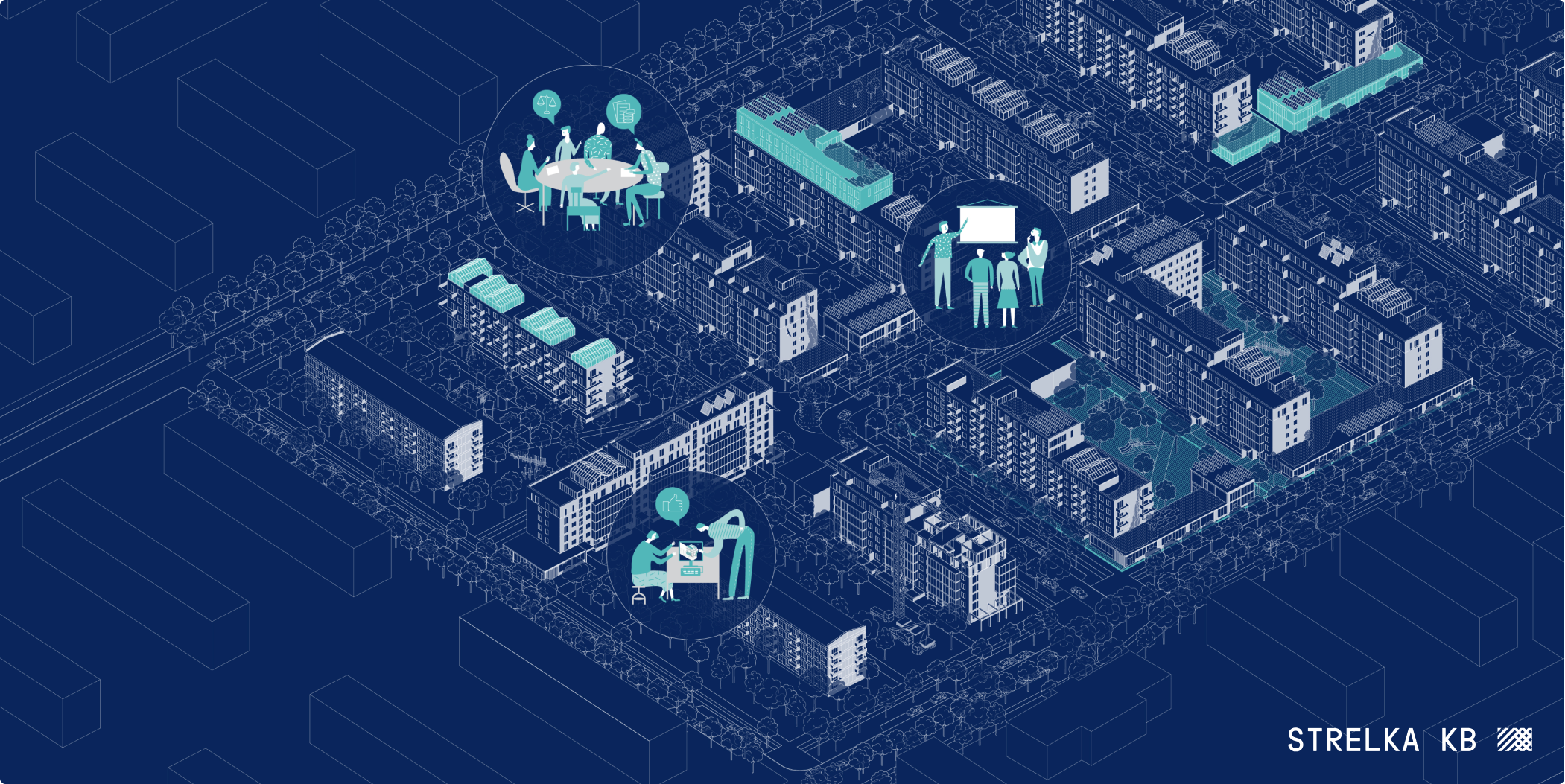
Governance solutions
Implementation of a strategic set of policies to create opportunities for an open dialogue between residents, city authorities and developers within the framework of the development of the district, as well as to ensure the introduction of new, flexible financial and non-financial instruments that allow the implementation of high-quality projects that meet the interests of all stakeholders.
Final results and outcomes
Potential result of the ESG-renovation:
- By 45% increase in the building footprint creating a more active neighbourhood
- Up to 30% of additional apartment areas
- Up to 30% increase of commercial and social areas
- From low quality apartments to comfort livable space
- Up to 25% density increase activating street life and improving security without overloading the infrastructure
- Up to 65% CO₂ emission savings due to energy-efficient improvement
- By 20% More neighbourhood connections through the engagement of new residents in participatory design and collective property management
- By 56% more residents will participate in the development of renovated districts
ESG New Urban Environment
